"Physics deals with matter and energy and their interactions in the fields of mechanics, acoustics, optics, heat, electricity, magnetism, radiation, atomic structure, and nuclear phenomena." (Merriam Webster definition)
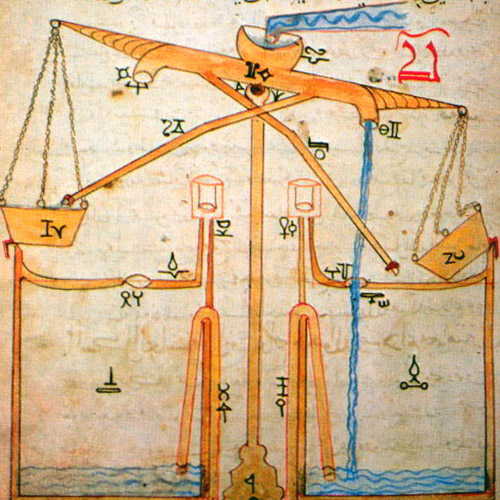
In a time when innovation had stalled in other parts of the world, Central Asian scholars were among the first to unite the experimental scientific method and practical concerns in mechanics and engineering. Owing to the importance of moving and controlling water in an arid environment, Central Asians made key advancements in the understanding of hydraulics and hydrodynamics. By the 9th century, Central Asian scholars familiar with the writings of Plato, Aristotle and Euclid had refuted their theories and begun to build an independent body of research in fields such as optics, thermodynamics and planetary science that would retain global influence into the modern era.
Scholars Who Studied Physics
 Ali Qushji
Ali Qushji